Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-01 Origin: Site








You will encounter several main types of automated guided vehicles in modern industry, each designed for specific tasks. These include automated forklifts, towing or tugger AGVs, unit load carriers, assembly line vehicles, and special purpose robots.
AGV Type | Description | Market Position |
|---|---|---|
Automated Forklifts | Load, unload, transport, and stack goods | Most popular AGV type |
Tow/Tractor/Tug | Tow multiple trailers efficiently | Largest revenue share in 2024 |
Unit Load Carriers | Carry lighter loads on top | Second-largest market segment |
Assembly Line | Handle assembly tasks | Niche market |
Special Purpose | Custom-built for unique needs | Smaller segment |
Understanding the types of automated guided vehicles helps you choose the right AGV for your workflow and maximize efficiency.
Automated guided vehicles come in various types like forklifts, towing vehicles, unit load carriers, and special-purpose robots, each designed for specific tasks to boost efficiency.
Forklift AGVs and towing AGVs improve safety and reduce labor costs by automating heavy load transport and stacking in warehouses and factories.
Laser-guided and vision-based navigation systems offer high accuracy and flexibility, allowing AGVs to adapt to complex and changing environments.
AGVs work best in stable, repetitive workflows with fixed routes, while autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) excel in dynamic settings with real-time obstacle avoidance.
Choosing the right AGV type and navigation method tailored to your facility’s needs can increase productivity, reduce errors, and improve workplace safety.

You need to understand the main types of automated guided vehicles to make smart decisions for your facility. Each type of AGV offers unique features and excels in different environments. Below, you will find a breakdown of the most common types of AGVs and how they work.
Towing vehicles, also known as automated tow tractors or tugger AGVs, play a vital role in material handling. You will see these robots pulling multiple carts or containers, much like a train engine. This design sets them apart from other types of automated guided vehicles that carry loads directly on their decks.
Automated tow tractors can tow loads exceeding 10,000 pounds, making them ideal for heavy goods movement in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers.
These AGVs follow fixed routes using laser sensors, magnetic strips, or vision-based navigation. You can rely on their precision and reliability in structured environments.
Automated tow tractors optimize material transport by pulling several carts at once. This feature boosts efficiency in large manufacturing facilities.
You will find that tugger AGVs require less operator training and offer a safer alternative to forklifts. They help reduce costs and improve safety in your operations.
Tip: If your workflow involves moving heavy loads over long distances, automated tow tractors provide a cost-effective and efficient solution.
Forklift AGVs, sometimes called robotic forklifts or autonomous forklifts, automate the lifting, stacking, and transport of pallets and goods. These robots operate without human intervention and integrate seamlessly with warehouse management systems.
Feature Category | Forklift AGVs (Robotic Forklifts) | Traditional Forklifts |
|---|---|---|
Operation Mode | Fully autonomous, 24/7 operation capability | Manually operated, dependent on operator skill and breaks |
Navigation & Precision | Laser SLAM technology, millimeter-level positioning, obstacle avoidance | Manual navigation, prone to human error |
Task Management | Smart scheduling, auto-assigns and prioritizes tasks | Manual task handling, requires human intervention |
Safety Features | 360° laser radar, sensors, emergency stop; reduces accidents by up to 90% | Higher accident rates, dependent on operator vigilance |
Power & Energy | Electric-powered, fast-charging, energy efficient | Diesel/petrol or electric, higher energy consumption |
Cost Considerations | Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs | Lower upfront cost, higher labor and maintenance expenses |
Flexibility & Adaptability | Rapid deployment, multi-task capability, quick attachment changes | Limited to fixed routes, retraining needed for new tasks |
You can use robotic forklifts for raw material transport, semi-finished product movement, and finished goods delivery. These AGVs handle pallet transport, automated storage and retrieval, and goods-to-person picking. Automotive plants use them for component delivery and just-in-time production. Automated forklifts reduce labor costs and improve safety, making them a popular choice in modern facilities.
Heavy load carrier AGVs move large and bulky items that other robots cannot handle. You will find several types of heavy load AGVs, each designed for specific tasks:
AGV Type | Typical Materials Transported | Usage Context |
|---|---|---|
Low Lifters | Large load carriers near ground level (e.g., pallets) | Transfer stations near the ground |
High Lifters | Pallets, mesh boxes | Handling Euro pallets and mesh boxes |
Reach Trucks | Heavy loads at heights up to 10 m | High stacking in warehouses |
Counterbalance | Large load carriers | Large loads with counterweight |
Very Narrow Aisle | Pallets in narrow aisles | Warehouses with narrow aisles |
Platform | Trolleys, small bins, shelves | Internal transport, high mobility |
Conveyor Deck | Pallets | Quick transfer to conveyor lines |
Multiple Pallets | Several pallets or load units simultaneously | Fork or conveyor deck based |
Lift & Carry | Small load carriers on trolleys, shelves, mesh boxes | Batch transport in production |
Picking | Load carriers within picking processes | Ergonomic and multi-order picking |
Heavy Duty | Heavy, shapeless loads up to 50 tons | Maximum flexibility, clamps or pliers |
Assembly Line | Production logistics materials | Automates production step transport |
You will see heavy load carrier AGVs in warehousing, production, assembly, and logistics centers. These robots handle everything from pallets and bins to steel coils and engines.
Automated guided carts, or AGCs, are compact robots designed for flexible material transport. You can program these AGVs to follow magnetic tape paths and use laser scanners for obstacle detection. Automated guided carts feature low-profile designs, customizable load capacities up to 4,400 lbs, and programmable speed settings.
Automated guided carts automate repeatable material handling tasks, such as connecting production islands or transporting materials from raw inputs to full assemblies.
You will find AGCs in industries like general manufacturing, warehousing, beverage, food storage, cold storage, retail, lumber, building materials, freight, and paper.
These robots integrate with fleet management software for route programming and fleet control.
Automated guided carts use RFID tags for location confirmation and instructions, and automatic charging systems for continuous operation.
Aspect | Evidence | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
AGC Role in Assembly Lines | Move components between workstations, transport tools and small parts, handle waste removal | Automates repetitive material handling, reduces manual labor and errors |
Operational Benefits | Operate 24/7 without fatigue, provide consistent performance, enable scalability | Increases throughput and operational capacity, reduces downtime |
Cost and Accuracy Improvements | Reduction in labor costs, fewer picking errors (up to 85% reduction), less product damage | Enhances accuracy, lowers operational costs in order picking and assembly |
Case Study: Automotive Parts Distribution | 45% reduction in picking errors, 30% increase in throughput, ROI in 28 months | Measurable efficiency gains in large facilities |
Case Study: E-commerce Fulfillment | 200% peak season capacity increase, 25% reduction in temporary labor costs | Flexibility and scalability during volume fluctuations |
Note: Automated guided carts maximize productivity and reliability in logistics operations, especially in assembly lines and order picking processes.
Unit load AGVs specialize in transporting single unit loads, such as totes or pallets. You will see these robots with decks optimized for handling unit loads. They interface with conveyors, palletizers, packaging stations, and other equipment.
Unit load AGVs support line feeding, work cell to work cell transport, and integration with automated systems.
These AGVs handle moderate payloads, typically pallets and totes, and move materials efficiently within manufacturing and warehouse environments.
Safety features include scanners, bumpers, and cameras for obstacle detection and safe operation.
Facility Type | Specific Tasks | Example/Company |
|---|---|---|
Manufacturing | Material transport, work-in-progress movement, product transport | Mitsubishi Electric using AGVs in smart factories |
Warehousing | Pallet handling (loading, unloading, stacking, transporting), inventory, order picking | Amazon fulfillment centers moving pallets; Global Logistics & Fulfillment using autonomous stockchasers |
Automotive Plants | Material transport, assembly line support, logistics optimization | Nissan deploying AGV fleets in assembly plants |
Logistics Centers | Trailer loading, shipment loading onto trailers | DHL using AGVs for trailer loading |
You will find unit load AGVs in manufacturing, warehousing, automotive, and logistics facilities. These robots improve workflow efficiency, reduce manual labor, and increase productivity.
Laser-guided AGVs use advanced navigation technology to operate in complex environments. You will see these robots equipped with LiDAR laser scanners that fire beams at reflective targets placed throughout the facility.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Navigation Technology | LiDAR laser scanners reflect off strategically placed targets. |
Position Calculation | Vehicle calculates its position accurately when at least three reflectors are visible. |
Accuracy | Laser triangulation is highly accurate and reliable. |
Installation Requirements | Reflector layout design and professional surveying required; setup is time-consuming and costly. |
Vehicle Design Constraints | Laser scanners mounted high for visibility; limits vehicle types that can use this method. |
Popularity and Comparison | Laser triangulation is one of the most popular and accurate AGV navigation methods. |
Pros | Reliable, highly accurate, efficient fleet management, easy digital route modification. |
Cons | Installation complexity and cost; limited vehicle compatibility. |
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, advanced manufacturing, power generation, iron and steel, and rail transportation benefit most from laser-guided AGVs. These robots offer high adaptability, real-time obstacle avoidance, and flexibility in dynamic settings. You can increase productivity, reduce labor costs, and improve safety with laser-guided AGVs.
Tip: If your facility requires precise navigation and operates in a complex environment, laser-guided AGVs provide unmatched accuracy and reliability.
You now have a clear overview of the main types of automated guided vehicles. Each AGV type offers distinct advantages, so you can select the best solution for your operational needs.

You will see automated guided vehicles transform manufacturing environments. AGVs automate the movement of materials, components, and finished products between workstations, storage areas, and shipping docks. You can use different types of AGVs for production parts delivery, pallet handling, and just-in-time manufacturing. AGVs replace manual forklifts and carts, reducing labor costs and workplace injuries. You can expect up to 33% higher throughput in large automotive plants after AGV integration.
AGVs use advanced navigation, such as laser and vision-based systems, to avoid obstacles and plan dynamic routes. You can customize AGVs with scissor lifts or rotators for ergonomic load handling. These robots automate repetitive and hazardous tasks, improving safety and operational efficiency.
Tip: You can boost production flow and minimize errors by deploying mobile picking robots for work-in-process movement and order picking.
Use-Case | Description | Productivity Improvement |
|---|---|---|
Production parts delivery | AGVs deliver parts to machines/workstations based on real-time feedback. | Increased throughput |
Pallet handling | AGVs move pallets between palletizer, warehouse, and shipping docks. | Enhanced safety, reduced labor |
Finished product handling | AGVs transport finished goods to storage or shipping, minimizing damage. | Better material handling consistency |
Picking | Mobile picking robots automate order picking and component retrieval. | Fewer errors, higher accuracy |
You will find AGVs essential in warehousing and distribution centers. AGVs transport goods between storage locations, picking stations, and shipping docks. You can integrate AGVs with automated storage and retrieval systems to speed up operations and reduce manual labor.
Mobile picking robots move shelves to workers, increasing picking speed and accuracy. AGVs handle loading and unloading tasks, improving inbound and outbound operations. You can optimize space utilization and safety by deploying AGVs for pallet picking and order picking.
AGVs support real-time monitoring and flexible production lines. You can scale AGV fleets to meet seasonal demand and adapt to labor shortages. Market data shows rapid AGV adoption, with strong ROI and efficiency gains in large facilities.
AGVs automate repetitive picking and pallet moving tasks.
Mobile picking robots reduce human errors and labor costs.
AGVs improve workplace safety and streamline inventory movement.
You can use AGVs for picking in high-volume industries like e-commerce and automotive.
You will discover AGVs in specialized industry applications beyond manufacturing and warehousing. Food and beverage companies use AGVs for bulk handling and internal transport in environments with changing humidity and temperature. You can customize AGVs with stainless steel construction and add barcode or RFID scanners for ingredient picking and weighing.
Hospitals deploy AGVs for meal delivery, linen transport, and waste removal. You can automate sterile supply delivery and pharmacy runs, freeing staff for patient care. Mobile picking robots use advanced navigation to avoid obstacles and reroute dynamically.
AGVs address unique challenges, such as continuous operation and safe human interaction. Wireless charging and fleet management software keep AGVs running efficiently. You can integrate AGVs with existing software for seamless mission assignment and real-time updates.
Note: You can solve complex logistics problems and improve efficiency by choosing AGV solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
Automated Guided Vehicles rely on different navigation skills to move safely and efficiently in your facility. You can choose from several guidance systems, each with unique strengths and limitations. Understanding how these systems work helps you select the best AGV vehicle for your needs.
Magnetic and inductive navigation methods use physical guides to direct AGV vehicles along set paths. You will find these systems in environments where routes rarely change. Here is a comparison of common magnetic and inductive navigation methods:
Navigation Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
Electromagnetic Navigation | Buried metal wires carrying low-frequency current generate magnetic fields detected by induction coils on AGV | Concealed guidewire, reliable, low interference, low cost | Difficult to change or expand path, complex wire laying |
Magnetic Stripe Navigation | Magnetic stripes on ground surface detected by sensors | Accurate positioning, easier to lay/change path than electromagnetic, lower cost | Easily damaged, requires maintenance, path changes require re-laying, no intelligent avoidance |
Magnetic Marker Navigation | Magnetic markers laid on ground detected by AGV | Good concealment, strong anti-interference, wear and chemical resistant | Affected by ferromagnetic substances, large construction for path changes, ground damage risk |
You will see AGV vehicles using induction coils to detect magnetic fields from wires or stripes. Magnet spot guidance uses sensors to measure magnetic flux density, allowing high-precision steering. Inductive wire guidance is popular for its stability and reliability. These systems work well in predictable environments, such as assembly lines or warehouses with fixed layouts.
Note: Magnetic and inductive navigation offer simple and reliable operation for repetitive tasks. However, you cannot easily change routes or adapt to obstacles. If your facility needs frequent layout changes, these systems may limit flexibility and scalability.
Optical and laser navigation methods give Automated Guided Vehicles advanced navigation skills. You can deploy these systems in dynamic environments where flexibility matters. Laser navigation uses LiDAR and SLAM technology to build digital maps and adjust routes in real time. Vision navigation relies on cameras and 2D codes for accurate positioning.
Navigation System | Accuracy | Flexibility | Cost | Environmental Requirements | Maturity Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Laser Navigation | Highly accurate (uses SLAM) | High flexibility, no extra equipment needed | Expensive | Requires good lighting and visibility | Mainstream, mature |
Vision Navigation | Accurate (uses SLAM with cameras) | Flexible, onboard camera-based | More cost-effective than laser | High environmental requirements | Less mature, developing |
Laser-guided AGV vehicles do not need physical changes to your facility. You can deploy them quickly and scale up as your needs grow. These systems allow dynamic rerouting and obstacle avoidance, which improves operational efficiency. Studies show that modern AGVs avoid obstacles in 80% of trips, reducing downtime and human intervention.
Tip: If you want to know how does an agv work in a changing environment, choose laser or vision navigation. These systems support easy deployment and adapt to new layouts without costly modifications.
You need to understand the differences between automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots before choosing a solution for your facility. AGVs follow fixed routes using physical guides like magnetic strips or floor markers. You will see these systems in structured environments where tasks rarely change. AGVs stop when obstacles block their path and often need human help to resume movement. In contrast, AMRs use advanced sensors such as LiDAR and 3D cameras. These robots map and navigate your facility in real time, avoiding obstacles and rerouting without assistance.
Feature | AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) | AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) |
|---|---|---|
Path Planning | Follow fixed, predefined routes using physical guides | Use real-time mapping and dynamic path planning |
Flexibility | Low flexibility; route changes require manual updates | High flexibility; adapt instantly to layout or route changes |
Obstacle Handling | Stop when encountering obstacles and wait for clearance | Detect and avoid obstacles autonomously in real time |
Navigation Technology | Use basic sensors and external guidance systems | Equipped with LIDAR, 3D cameras, and AI-driven SLAM technology |
Environment Suitability | Best for structured, predictable environments | Ideal for dynamic, unpredictable environments |
Autonomy Level | Limited autonomy; rely on pre-set instructions | High autonomy; make navigation decisions independently |
AGVs excel at repetitive tasks in manufacturing plants, especially automotive OEMs. You will find over 60% of AGV vehicles in factories, where they improve consistency and reduce cycle times. AMRs dominate warehousing, e-commerce, and healthcare. In 2023, smart warehouses deployed over 80,000 AMRs, boosting space utilization by 45% and cutting order fulfillment times by up to 70%. AMRs offer greater operational flexibility and efficiency, making them ideal for dynamic workflows.
Tip: If your facility has a stable layout and needs predictable, repetitive automation, AGVs provide cost-effective solutions. For changing environments and flexible tasks, AMRs deliver superior adaptability.
You should consider several factors when selecting between AGVs and AMRs for your workflow. AGVs work best for predictable, repetitive tasks in facilities with fixed layouts. You need to install wires, magnetic strips, or markers, which increases setup time and cost. AGVs require clear pathways and may need workplace modifications. AMRs adapt to changing layouts without physical guides. These driverless mobile robots use sensors and AI to detect obstacles and reroute instantly.
Factor | AGV Characteristics | AMR Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Task Nature | Best for predictable, repetitive tasks | Suited for dynamic, flexible tasks |
Facility Layout | Requires stable, fixed layouts; changes need infrastructure modifications | Adapts to changing layouts without physical changes |
Navigation & Obstacle Handling | Follows fixed paths; stops when obstacles encountered, causing delays | Uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles, rerouting autonomously |
Safety | Basic safety features; less suited for close human interaction | Advanced safety; better for environments with human-robot interaction |
Infrastructure & Deployment | Needs installation of wires, magnetic strips, or markers; higher setup time and cost | Quick deployment; no physical infrastructure needed |
Scalability & Flexibility | Limited scalability; changes are costly and time-consuming | Highly scalable and flexible; software updates enable changes |
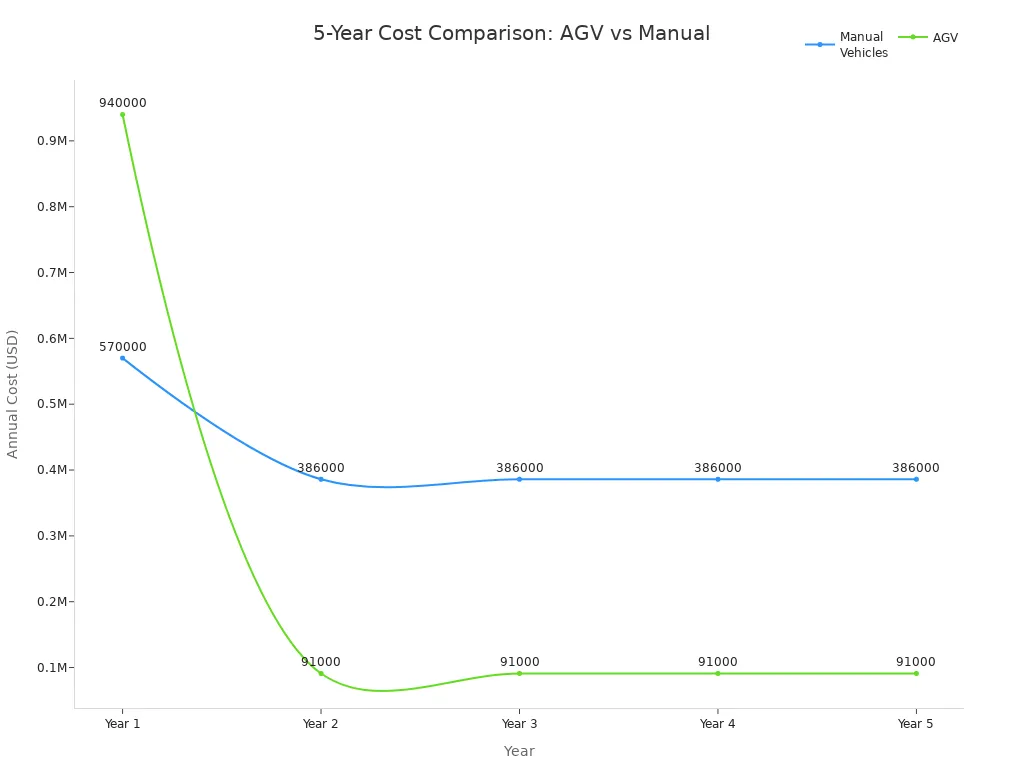
AGVs require a higher initial investment, but you save on labor and maintenance over time. AMRs offer quick deployment and long-term scalability. You can update tasks and routes with software, making AMRs ideal for facilities with frequent changes. Autonomous mobile robots comply with modern safety standards, supporting safe human-robot interaction in busy environments.
Note: Choose AGVs for stable, repetitive workflows and AMRs for dynamic, flexible operations. Both solutions improve productivity, but AMRs provide unmatched adaptability for modern logistics and manufacturing.
Choosing the right types of Automated Guided Vehicles for your facility shapes your success. You improve operational efficiency and reduce manual labor when you match AGV vehicle capabilities to your workflow, load capacity, and navigation needs. Advanced safety features, such as emergency stops and laser scanners, help minimize workplace accidents.
Remember to integrate AGVs with warehouse management systems, automate data collection, and optimize picking processes. Evaluate your facility layout and collaborate with experienced suppliers to ensure smooth deployment and reliable performance.
You use Automated Guided Vehicles to move materials, products, and pallets in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. These AGV vehicles improve safety, reduce labor costs, and boost productivity in your facility.
Tip: Automated Guided Vehicles work best for repetitive tasks and structured environments.
Automated Guided Vehicles follow fixed paths using sensors or guides. Autonomous vehicles, like AMRs, use advanced mapping and AI to navigate freely. You choose AGV vehicles for predictable workflows and autonomous vehicles for flexible, changing layouts.
Feature | AGV Vehicle | Autonomous Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
Navigation | Fixed routes | Dynamic mapping |
Flexibility | Low | High |
Yes, you can use an Autonomous forklift as an AGV vehicle. Autonomous forklifts automate lifting, stacking, and transporting pallets. You deploy these AGV vehicles in warehouses and manufacturing plants to improve efficiency and safety.
You see Automated Guided Vehicles use magnetic strips, laser scanners, and cameras for navigation. AGV vehicles rely on these systems to follow routes, avoid obstacles, and operate safely in your facility.
Note: Laser-guided AGV vehicles offer the highest accuracy for complex environments.
Automated Guided Vehicles streamline material flow, reduce manual labor, and minimize errors. You increase throughput and safety by deploying AGV vehicles and autonomous forklifts in your warehouse.
Automated Guided Vehicles handle repetitive transport tasks.
Autonomous forklifts stack and move pallets efficiently.