Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-27 Origin: Site








You want a clear path for adding agvs to your facility. Automated guided vehicles deliver proven results, with over 35% of U.S. warehouses already using agvs and more than 80% of large logistics hubs globally adopting robotic automation. You can expect benefits like increased productivity, enhanced safety, and reduced labor costs. AGVs adapt to hazardous environments, offer long operational hours, and support scalable automation. Careful planning, robust integration, and staff training help you realize the full benefits of agvs.
Common benefits of agvs:
Improved accuracy and efficiency
Enhanced safety through sensors
Reduced error rates
Start by assessing your facility’s needs, workflows, and safety standards to ensure readiness for AGV integration.
Choose the right AGV types and navigation methods that fit your tasks and environment for reliable and efficient operations.
Prepare your facility layout with clear navigation lanes, marked pathways, and safety zones to support smooth and safe AGV movement.
Integrate AGVs with your warehouse systems using middleware and secure data flow to optimize task management and coordination.
Train your staff thoroughly on AGV operation and safety, and monitor performance continuously to improve efficiency and maintain safety.
You should begin your assessment by gathering detailed information about your current operations and logistics requirements. Communication among all stakeholders is critical. Involve logistics managers, maintenance teams, and IT staff to ensure everyone understands the impact of adding agvs. Evaluate your facility’s readiness by checking building maintenance, infrastructure, and IT systems. Assess risk management strategies, including financial and operational risks, to avoid unexpected issues during automation.
Tip: Make sure your facility complies with safety standards such as ANSI/RIA R 15.08. Test agv response to obstacles, collision avoidance, and electromagnetic compatibility to ensure safe operation.
Review your existing workflows to identify tasks that automated guided vehicles can automate. Focus on repetitive material movement, regular delivery of stable loads, and operations that require on-time delivery and tracking. The table below highlights common applications of agvs in various industries:
Facility Task Category | Description and Examples |
|---|---|
Pallet Handling | Loading, unloading, stacking, and transporting pallets in manufacturing and distribution facilities. |
Work-in-Progress Movement | Moving unfinished materials between production stages or from warehouse to production lines. |
Trailer Loading | Loading goods onto trailers for shipment, often using conveyor belts or lifts. |
Raw Material Handling | Moving raw materials from receiving to production lines. |
Finished Product Handling | Moving finished goods from manufacturing to storage or shipping. |
Roll Handling | Transporting and stacking rolls in paper mills, printing plants, and steel producers. |
Container Handling | Moving sea containers in port terminals. |
Towing/Pulling Carts & Trailers | Using towing agvs to pull carts or trailers, moving multiple smaller loads. |
Use discrete event simulation or efficiency evaluation tools to model how agvs will impact your facility. Consider how asrs and automated storage and retrieval systems interact with agvs to support efficient material flow and productivity.
Set clear, measurable goals for your agv project. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) such as throughput, labor savings, return on investment, cash flow, productivity, quality, accuracy, consistency, reliability, and employee satisfaction. Use telematics and warehouse management systems to track these metrics. Regularly revisit your business case and update your goals as your automation project evolves.
Note: Training and technical education for your staff and technicians are essential for smooth operation and long-term success.
By following these steps, you ensure that your facility is ready for agvs and that your automation project delivers maximum efficiency and value.
Designing automated guided vehicle systems requires you to select the right agv types, navigation methods, and custom features for your facility. Careful planning ensures that agvs deliver maximum efficiency and reliability in your operations.
You can choose from several agv types, each designed for specific tasks and environments. The table below summarizes the most common types of automated guided vehicles used in industrial settings:
AGV Type | Description | Industrial Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
Unit Load AGVs | Handle and move large or palletized loads with advanced navigation; used in manufacturing and warehousing. | Amazon uses unit loaders in fulfillment centers to move pallets efficiently. |
Towing AGVs | Driverless vehicles that tow heavy carts or trailers; capable of hauling multiple carts simultaneously. | Cyngn’s Automated Tugger to transfer finished goods, towing 12,000-20,000 lbs. |
Automated Guided Carts (AGCs) | Compact vehicles transporting smaller quantities; ideal for material transport and assembly line feeding. | Boeing uses AGCs in aircraft manufacturing to move components along assembly lines. |
Custom AGVs | Tailored AGVs designed for specific needs with specialized features and integration capabilities. | General Motors employs over 75 custom AGVs in automotive manufacturing for material delivery. |
You should select agvs based on your load size, workflow, and integration needs. For fixed routes and repetitive tasks, agvs offer more predictable performance than AMRs (autonomous mobile robots).
Navigation technology determines how agvs move through your facility. You can select from several methods, each with unique strengths and limitations. The table below compares popular navigation systems:
Navigation Method | Accuracy | Reliability | Key Advantages | Key Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Laser Triangulation (LiDAR with reflectors) | Highly accurate | Highly reliable if reflectors are well installed | Digital routes allow flexible fleet management; high accuracy | Installation of reflectors is time-consuming and costly; reflector layout critical |
Magnetic (Electromagnetic field, Magnetic stripe) | Highly accurate | Highly reliable; not affected by dynamic environment changes | Concealed guidewire (electromagnetic); relatively low cost (magnetic stripe) | Difficult and disruptive to install or change paths; magnetic stripes prone to damage and require maintenance |
Wire (Embedded wires) | Highly accurate | Highly reliable | Simple and reliable navigation principle | Installation is disruptive and costly; path changes require re-laying wires |
Optical (Vision guidance, 2D code) | Accurate positioning | Less reliable due to environmental sensitivity | Flexible and easy to install; no infrastructure changes needed | Affected by lighting, ground texture, and environmental conditions; requires regular maintenance for codes |
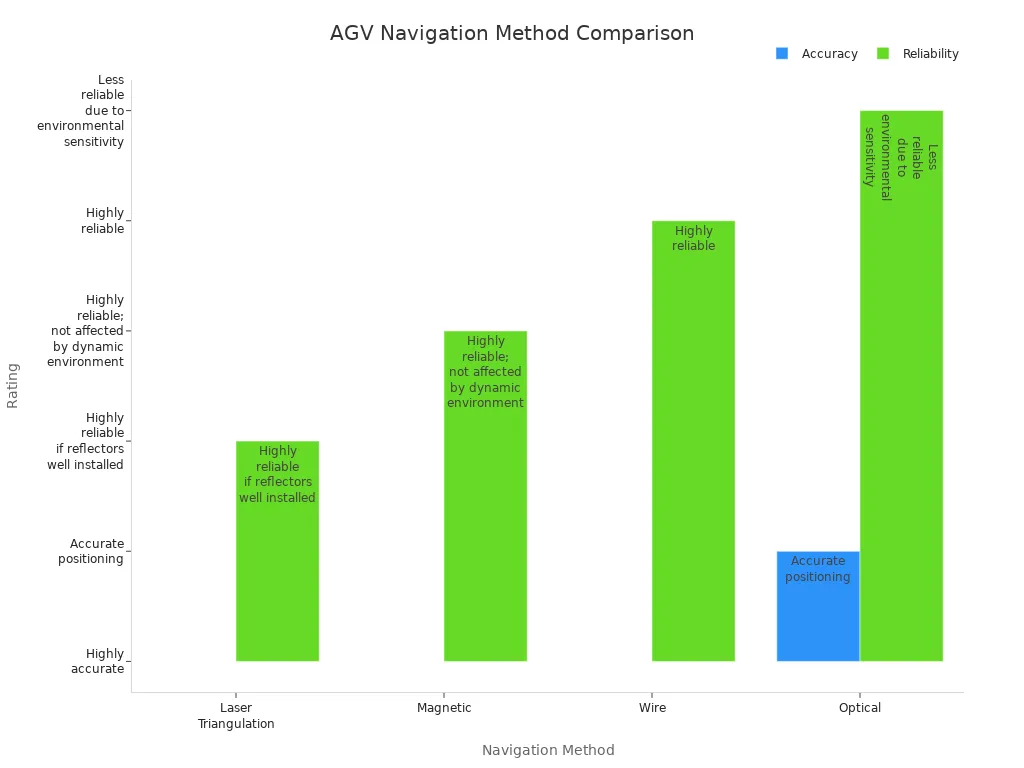
Laser and magnetic navigation methods provide high accuracy and reliability, making them ideal for asrs and automated guided vehicle systems with fixed routes. Optical systems offer flexibility but may require more maintenance.
You can tailor agvs to fit your unique facility requirements. Customization options include:
Specialized tooling such as scissor lifts, rotators, or turntables for unique material handling.
Adaptable navigation technologies, including laser, magnetic, or vision-guided systems.
Adjustable load capacities and agv sizes to match your workflow.
Industry-specific features like cleanroom compatibility or explosion-proofing.
Integration with asrs, manufacturing, or assembly management systems for synchronized operations.
Enhanced safety features, including collision avoidance, emergency stops, and warning lights.
User-friendly interfaces to simplify operator training.
Advanced technologies such as AI, IIoT integration, and eco-friendly power options.
Tip: Custom agvs help you maximize efficiency, safety, and productivity by aligning with your facility’s environment and operational goals.
By focusing on the right agv types, navigation methods, and customization, you ensure your automated guided vehicle systems deliver reliable performance and support continuous improvement in your facility.

You must adapt your facility to support agv movement and efficiency. Start by creating navigation lanes tailored to the agv guidance system. Separate agv routes from forklift and other equipment paths to prevent collisions and traffic jams. Consider the speed and maneuverability of each agv when planning the layout. Upgrade your floor plan to optimize agv performance and minimize bottlenecks. Designate operating zones where agvs can work exclusively, reducing interference from other vehicles. Establish home bases or parking areas for agvs, keeping these spaces clear of pallets and containers. These steps help you maintain a clear pathway for agvs and support safe, reliable operations.
Create navigation lanes for agvs based on guidance technology.
Separate agv routes from other equipment.
Designate operating zones and home bases.
Upgrade floor plans for agv speed and maneuverability.
Marking pathways is essential for guiding agvs and ensuring safety. Select the right type of floor tape for your agv navigation system and facility environment. Options include solid-colored vinyl for visibility, magnetic tape for sensor-based navigation, and matte finish tape for durability. Use color-coding to separate human and vehicle traffic and define clear pathway boundaries. Regularly inspect and clean marked pathways to prevent debris from interfering with agv sensors. Replace damaged tape sections promptly to maintain navigation accuracy. Troubleshoot routing issues by checking accessibility and refreshing path links. Manage intersections by creating control areas to avoid deadlocks and traffic conflicts.
Choose suitable floor tape for agv navigation.
Use color-coding for safety and route identification.
Inspect and maintain marked pathways.
Control traffic at intersections.
Tip: Safety markings and clear pathway definitions help prevent accidents and support efficient agv movement.
Establishing safety zones protects both workers and agvs. Classify agv operating zones based on clearance and safety device presence. Operating zones require at least 0.5 meters of clearance and active safety devices. Hazard zones need speed limits and audible warnings. Restricted zones limit access to trained personnel and require emergency stop devices. Mark all zones with floor markings, signs, and lights to avoid confusion. Include escape routes so employees can leave aisles safely. Equip agvs with visible lighting, such as bright blue LEDs, to alert workers. Train all personnel on agv safety and conduct a final audit before starting operations. These measures ensure a clear pathway and safe coexistence of agvs and people.
Classify operating zones: operating, hazard, restricted, confined, and load transfer.
Mark zones with safety markings and signs.
Provide escape routes and visible agv lighting.
Train staff and audit safety before launch.
You need to connect automated guided vehicle systems with your Warehouse Management System (WMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms. This integration allows you to send instructions to each agv, such as task locations, pick and place commands, and scheduling. Most agvs rely on APIs to communicate with these systems, enabling real-time coordination and efficient task management. You may encounter challenges because many agv suppliers do not offer deep integration with WMS, ERP, or Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). Hardware distributors and typical OEMs often provide robots and fleet management software but lack full system integration. Full-service OEMs deliver end-to-end solutions, but these can be rigid and costly. Middleware solutions bridge these gaps, allowing seamless communication between agvs, asrs, and enterprise systems. Middleware also supports scalability, so you can add more agvs without major infrastructure changes.
Tip: Use middleware to synchronize material movements with inventory control and production schedules, optimizing your warehousing operations.
You must ensure smooth data flow between agvs, robots, and warehouse systems. Interface protocol incompatibility, such as Modbus/TCP versus OPC UA, can disrupt data synchronization. Integration with WMS and MES enables automatic task allocation, real-time path planning, and collaborative robot operations. You should define detailed design data for all warehouse movements under agv control, including inbound and outbound volumes, raw material movements, and replenishments. Multi-departmental design approvals help you address complex integration challenges and avoid costly disruptions. Capture and report downtime data to identify and resolve operational issues quickly.
Protecting your systems and data is essential during agv integration. Middleware manages real-time data and controls access between agvs and enterprise systems, ensuring data integrity and security. You must secure communication channels and restrict access to authorized personnel. Regularly update software and monitor system activity to prevent unauthorized access. Integrating agvs with automated storage and retrieval systems, conveyor lines, and other robots requires strong compatibility and precise control command transmission. These steps help you maintain efficient, secure, and intelligent operations in your facility.
Installing and testing agvs in your facility requires careful planning and attention to detail. You need to ensure that automated guided vehicles operate smoothly, integrate with your existing systems, and deliver reliable performance from day one. This section guides you through the essential steps for setup, pilot testing, and troubleshooting.
You should begin by preparing your facility and infrastructure for agvs. Follow these steps to ensure a successful setup:
Gather Information and Assess Infrastructure
Evaluate your current warehouse IT setup. Check your warehouse management systems, wireless networks, and system interfaces. This assessment helps you choose the right automated guided vehicles and identify any upgrades needed for smooth operation.
Define Your Processes
Map out all operational processes. Use real-time simulations or CAD layouts to plan travel routes, vehicle properties, and charging stations. This step ensures that agvs fit seamlessly into your workflow.
Prepare for Implementation
Install and test agv software. Program master computers and PLC interfaces. Prepare the physical environment by installing electrical wiring, signal units, and navigation reflectors. These preparations create a solid foundation for your agvs.
On-Site Installation and Integration
Train your operators and key users on agv operation, safety, and troubleshooting. Conduct functionality tests and fine-tune travel paths. Integrate agvs with conveyor technology and other automated systems to ensure smooth material flow.
Start Operation
Begin the commissioning phase with start-up assistance. Address any operator concerns and perform quality assessments. This phase helps you catch and resolve issues early.
Tip: Plan for ongoing maintenance and support. Reliable 24/7 support ensures continuous agv operation and minimizes downtime.
Pilot testing helps you validate the performance and reliability of your agvs before full-scale deployment. You should:
Run initial tests to check navigation accuracy and obstacle detection.
Test communication between agvs and your warehouse management systems.
Monitor how agvs interact with other automated systems, such as conveyors or storage units.
Evaluate task completion times, route efficiency, and battery usage.
Collect feedback from operators and adjust workflows as needed.
A structured pilot phase allows you to identify and fix issues before they impact your operations. Use telematics and fleet management software to track agv performance and gather usage statistics.
Test Area | What to Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Navigation Accuracy | Path following, obstacle avoidance | Prevents collisions and delays |
System Communication | Data exchange with WMS and other systems | Ensures smooth task execution |
Task Performance | Speed, load handling, battery life | Confirms operational efficiency |
Operator Feedback | Ease of use, safety, workflow integration | Improves user acceptance |
Note: Design testable requirements and use Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to predict potential failures. This approach helps you prevent defects before they occur.
During installation and testing, you may encounter challenges. Effective troubleshooting ensures your agvs deliver consistent results. Common strategies include:
Checking path definitions to resolve navigation errors or unreachable destinations.
Using routing accessibility visualization tools to spot breaks in path links.
Creating special accumulation types for close-quarter intersections to manage control areas.
Disabling accumulation in complex intersections and adjusting control area deallocation timing to prevent traffic conflicts.
Real-time monitoring with fleet manager software or SCADA systems to detect and resolve issues quickly.
Tracking usage statistics to identify recurring errors and assess system performance.
Modifying projects to add or adjust vehicle routes and pick/drop locations as your needs change.
Scheduling regular maintenance for agv components such as wheels and sensors.
Tip: Plan for future expansion by choosing multi-brand fleet management platforms. This approach reduces complexity and risk as you scale up your agv fleet.
By following these steps, you ensure that automated guided vehicles integrate smoothly with your facility. Careful setup, thorough pilot testing, and proactive troubleshooting help you achieve reliable, efficient, and safe agv operations.
You need a robust training program to ensure safe and efficient AGV operation. Tailor your training to different roles, such as system overseers, direct operators, and human workers who share the workspace. Cover essential topics like operational procedures, diagnostics, troubleshooting, and software interface use. Onboarding and orientation help new employees understand advanced material handling and AGVs. Hands-on sessions, including simulations or real machine use, build confidence and practical skills. Strong safety training should address hazard identification, risk assessment, proper use of PPE, emergency response, and safe AGV operation. Regular refresher courses and safety checks keep everyone up to date. OEM-provided training ensures you receive accurate instruction on specific AGVs. Measure training effectiveness by tracking knowledge retention, on-the-job performance, and reductions in safety incidents.
Tip: Foster a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing to keep your team engaged and informed.
You must follow strict safety protocols when working with AGVs. Start by complying with OSHA and ANSI/ITSDF standards. Mark hazard and restricted zones clearly with signs, stripes, and lights. Train all personnel to recognize these zones and understand the risks. Use audible and visual alarms at blind corners to alert human workers of approaching AGVs. Maintain minimum guidepath clearances, such as 0.5 meters on both sides, to prevent collisions. Only authorized personnel should perform maintenance or repairs, always following manufacturer guidelines. Equip AGVs with 360° collision avoidance systems, emergency stop buttons, and safety-rated sensors. These features help prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation. Encourage safe practices, such as staying alert, maintaining safe distances, and never overriding safety devices.
You can optimize collaboration between AGVs and human workers by leveraging advanced technology and clear communication. AGVs use 360° sensors to detect obstacles and stop when people are too close, allowing safe interaction. Real-time data exchange supports dynamic route planning and workflow optimization. Human workers bring adaptability and decision-making skills, while AGVs handle repetitive and physically demanding tasks. This partnership reduces fatigue and injury risk. Collaborative systems, such as goods-to-person workflows, improve efficiency and accuracy. Integrating AGVs with other robots and warehouse systems creates balanced operations and smarter workflows. Predicting human movement using schedules and real-time location data allows AGVs to adjust routes, further enhancing safety and productivity.
You should approach the go-live phase with careful planning and gradual scaling. Start with on-site installation and integration. Measure the navigation environment, complete network integration, and test all systems. Train your employees on AGV operation and safety. Fine-tune the AGVs during live operation by testing routes and correcting any deviations.
Begin the commissioning phase with start-up assistance for your operators. Provide on-the-job training and address any concerns. Ensure smooth interaction between personnel and AGVs. Complete this phase with a quality assessment of the automated system.
After launch, maintain continuous support. Offer a 24/7 hotline staffed by AGV experts, remote troubleshooting, and on-site repairs as needed. This support keeps your systems reliable and minimizes downtime.
You need to monitor AGV performance closely after launch. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) give you real-time visibility into vehicle locations, task progress, battery levels, and maintenance status.
MES platforms let you intervene, reroute tasks, and adjust priorities based on live data. Fleet Management Systems (FMS) and Robot Control Systems (RCS) coordinate tasks, routes, and sensor data to optimize fleet operations.
You can use dashboards to track efficiency improvements, transport speed, idle time, and battery management. Communication standards like VDA 5050, OPC UA, and MQTT ensure secure data exchange between systems.
Tip: Use web-based visualization tools to monitor AGVs and robots in real time, helping you spot issues quickly and keep operations running smoothly.
You should focus on continuous improvement to maximize efficiency and productivity. Develop standard work for material handlers and create predictable routes for AGVs. Standardize processes, define roles, and keep areas orderly.
Simulate AGV routes with manned carts before full deployment to reduce disruptions. Integrate AGVs with ERP and MES systems to synchronize production and get real-time feedback.
Upgrade navigation technologies to allow flexible route changes and minimize infrastructure changes. Regularly review performance data and adjust workflows to improve efficiency.
Note: Continuous improvement ensures your systems adapt to changing needs and deliver long-term value.
You can achieve lasting benefits by following a structured approach to AGV implementation. Start by assessing your facility’s readiness, planning workflows, and involving your team. AGVs deliver benefits such as improved employee well-being, reliable operations, and enhanced inventory accuracy. Facilities report low maintenance needs, stable costs, and increased automation efficiency.
Remember, ongoing staff engagement and continuous improvement help you maximize the benefits of agvs. Now is the time to assess your readiness and unlock the full benefits of agvs in your facility.
Automated Guided Vehicles follow fixed routes using sensors or markers. Autonomous vehicles use advanced navigation and can adapt to changing environments. You use AGV vehicles for predictable tasks. Autonomous forklifts and robots handle dynamic operations.
You can connect Automated Guided Vehicles to your WMS or ERP using APIs or middleware. AGV vehicles share data with autonomous vehicles and autonomous forklifts. Integration improves task management and inventory accuracy.
You must train staff, mark safety zones, and use collision avoidance systems. Automated Guided Vehicles and AGV vehicles need regular maintenance. Autonomous vehicles and autonomous forklifts require emergency stop buttons and warning lights.
You select Automated Guided Vehicles based on load size, route complexity, and workflow needs. Autonomous forklifts work best for flexible tasks. AGV vehicles suit fixed routes. Autonomous vehicles offer advanced navigation for changing environments.
You inspect sensors, wheels, and batteries regularly. AGV vehicles need software updates and safety checks. Autonomous vehicles and autonomous forklifts require diagnostics and calibration. Preventive maintenance reduces downtime and improves reliability.